Description
Prolia 60 mg Solution for Injection in Pre-Filled Syringe | Ahmed Medico
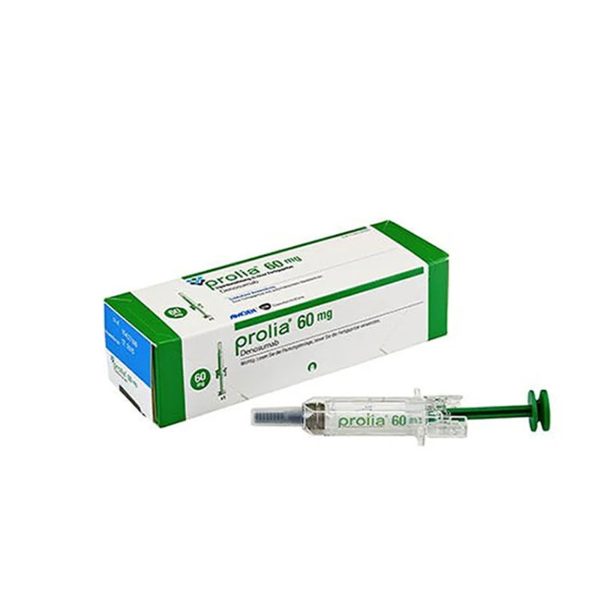
Prolia 60 mg injection in a pre-filled syringe gives you a reliable option for managing osteoporosis and preventing bone loss. The active ingredient, denosumab, is a monoclonal antibody that targets the root cause of bone resorption. When you choose Prolia, you access a therapy trusted by healthcare providers worldwide for its effectiveness in reducing fracture risk and improving bone density.
For patients dealing with cancer-related bone complications, alternative treatments such as xgeva injection price in pakistan may also be considered under specialist guidance.
How Prolia Injection Works
Prolia works by blocking the RANK ligand, a key protein that activates osteoclasts, the cells responsible for breaking down bone tissue. By inhibiting this pathway, Prolia helps you maintain stronger bones and significantly lowers your risk of fractures. This targeted action sets Prolia apart from traditional osteoporosis treatments, offering you sustained protection with just two injections per year.
Key Benefits of Prolia
- Convenient Dosage: You receive Prolia as a subcutaneous injection once every six months, making it easier to stay on track with your treatment.
- Proven Fracture Prevention: Clinical studies show Prolia reduces vertebral fractures by 68%, hip fractures by 40%, and non-vertebral fractures by 20%.
- Suitable for High-Risk Patients: If you have kidney disease or cannot tolerate oral osteoporosis medications, Prolia provides a safe and effective alternative.
Uses of Prolia 60 mg Solution
Doctors prescribe Prolia for:
- Osteoporosis Treatment: For postmenopausal women and men at high risk of fractures.
- Preventing Bone Loss: During hormone therapy for breast or prostate cancer.
- Managing Bone Density: Increasing bone mineral density at the spine and hip.
In hormone-dependent cancer cases, physicians may also recommend therapies like zoladex 3.6 mg injection as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Storage and Handling
Store Prolia in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C) to maintain its effectiveness. Never freeze the pre-filled syringe and keep it protected from light in its original carton. Before use, allow the syringe to reach room temperature for 15–30 minutes. Once removed from refrigeration, use within 30 days.
Precautions and Warnings
- Hypocalcemia Prevention: Your doctor will check your calcium levels before starting Prolia. You must take daily calcium and vitamin D supplements during treatment.
- Kidney Disease: If you previously have advanced kidney disease, your doctor will closely monitor you for hypocalcemia, especially during the first month.
- Dental Issues: Maintain good oral hygiene and inform your dental care expert about your medication before any dental procedures.
Possible Side Effects of Prolia
You may experience back pain, muscle pain, or skin infections. Rare but serious side effects include severe hypocalcemia, atypical femoral fractures, and osteonecrosis of the jaw. Contact your healthcare specialist immediately if you notice unusual thigh or jaw pain.
Prolia Injection Price in Pakistan
The Prolia 60 mg price in Pakistan ranges from PKR 40,000 to PKR 50,000, depending on the pharmacy and current exchange rates. At Ahmed Medico, you receive competitive pricing on this imported medication, with strict cold-chain management to ensure product quality.
Where to Buy Prolia 60 mg Solution in Pakistan
You can buy Prolia 60mg injection in Pakistan through Ahmed Medico’s secure online platform. We ensure privacy, genuine products, and temperature-controlled delivery to maintain the medication’s effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Prolia 60 mg Solution for Injection?
Prolia is a prescription medication containing denosumab, a monoclonal antibody used to treat osteoporosis and prevent bone loss. It comes as a pre-filled syringe for subcutaneous injection, administered every six months by healthcare professionals.
How Prolia Injection Works?
Prolia blocks the RANK ligand, preventing osteoclast activation and bone resorption. This targeted mechanism increases bone density and reduces fracture risk, providing you with sustained protection against osteoporosis-related fractures.
Why Choose Prolia 60mg Injection?
Prolia offers convenient twice-yearly dosing, proven fracture reduction, and suitability for patients with kidney disease or intolerance to oral medications. Clinical studies confirm significant improvements in bone density and long-term fracture prevention.
Why Choose Ahmed Medico?
Ahmed Medico provides authentic imported medications, with strict cold-chain storage, competitive pricing, and reliable nationwide delivery. As Pakistan’s leading online pharmacy, we guarantee genuine products and professional support for your bone health management.
How to Use Prolia 60 mg Solution?
A healthcare professional administers Prolia as a subcutaneous injection in your upper arm, thigh, or abdomen every six months. You must take prescribed calcium and vitamin D supplements daily and attend regular follow-up appointments.
Where to Buy Prolia 60 mg Solution in Pakistan?
You can purchase authentic Prolia through Ahmed Medico’s secure online platform. We offer verified ordering, proper temperature-controlled handling, and reliable delivery services across Pakistan, ensuring pharmaceutical quality standards.